Legacy Tool Registration Methods
Important
Workflows and tools added to Dockstore via our legacy registration methods do not automatically stay in sync with their source repository. Instead, someone with access to the entries on Dockstore must periodically log into Dockstore and press a button to trigger a refresh. Although this process is quick and will bring in all new tags, commits, and branches with the click of a button, it is easy to forget to do this and might not be appropriate for frequently-updated tools and workflows. For this reason, we recommend using GitHub App registration instead.
Differences Between Legacy Tools and GitHub App Tools
If you would prefer not to use GitHub App registration for your tool, you can instead use one of these methods. Be aware, however, that these legacy methods result in the creation of a “legacy tool” which works differently compared to a GitHub App registered tool. The basics are summarized in the table below, and we have docs explaining the historical reasons for the differences too.
Differences |
Legacy Tool |
GitHub App Tool |
|---|---|---|
Use case |
User owns the Docker image |
User doesn’t need to own the image (or their tool does not use Docker) |
Dockerfile |
Dockerfile required |
Dockerfile not required |
Versioning |
Based on image’s tags |
Based off of branches/tags from git repository |
Path |
Docker container location |
GitHub repository location |
Dockstore CLI |
Run in tool mode |
Run in workflow mode |
Legacy Tool Registration: Assumptions
Important
These methods require that you have created or have permissions to a Docker image. If that is not the case, consider reading Getting Started with Docker to create one, or switching to GitHub as your code hosting platform so you can use GitHub App registration.
To use the following registration options, you need have your Dockerfile and your CWL file in GitHub, have set an autobuilding Docker image, and have linked your accounts to Dockstore. We describe this process with a CWL tool in the Getting Started with Docker and Getting Started with CWL tutorial.
Legacy Tool Registration Methods
Option A: Quick Registration via the Web UI
In the authenticated Web UI, navigate to ‘My Tools’ to begin managing Docker images imported through your linked account(s). These pages will allow you to quickly register tools that follow a particularly simple format (look below to manual registration for more complex formats). For quick registration, we look through your Quay.io images and see if any are set up as automated builds. Using those to track back to your GitHub, Bitbucket, or GitLab accounts, we list all pairs of Docker images with git repositories that you have access to on those services. When we discover both of these, we create an unpublished entry in the interface below. We consider these tools as automated since new versions of the tool will be automatically added.
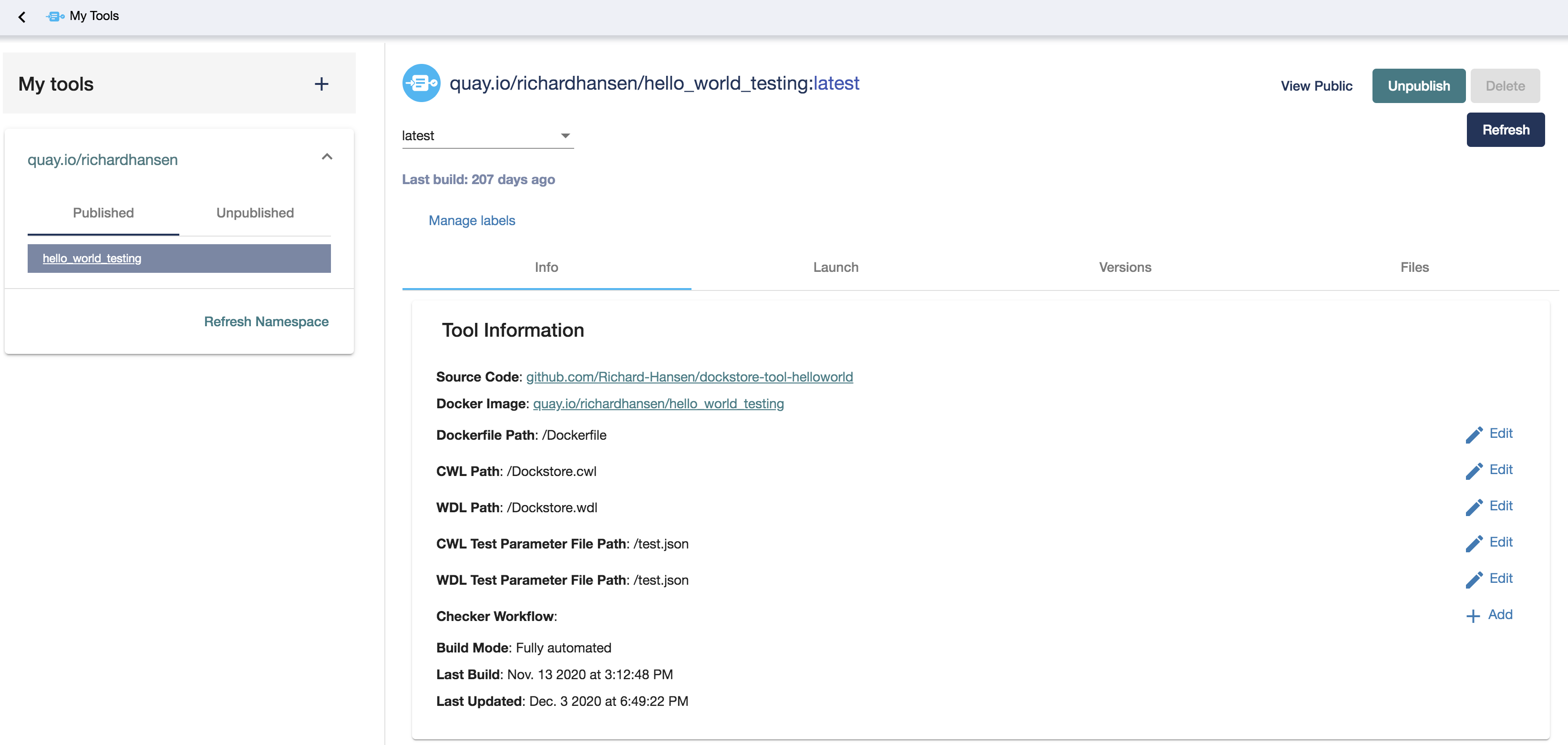
My Tools
The left side menu is a list of all image repositories associated with
the user, grouped alphabetically by namespace. Each tool is named
after the docker location of the associated Docker image, in this
example, quay.io/collaboratory/dockstore-tool-bamstats. Detailed
information and links for each tool are located on the ‘Info’ tab. The
‘Launch’ tab includes commands for launching the tool locally with the
Dockstore CLI. Settings such as the path to the Dockerfile and the
Descriptor files can be modified on a per-tag basis in the ‘Versions’
tab. The Dockerfile, CWL/WDL Descriptor and test parameter files may be
viewed in the ‘Files’ tab, by the Version tag (corresponding to a Git
tag/branch). Finally, ‘Manage labels’ (located above the tabs) allows
you to add/edit keywords that you want to be associated with a tool
for efficient searching and grouping.
We also look for /test.cwl.json and /test.wdl.json in the git
repositories on quick registration. These are the default test parameter
file locations. Whenever a new version is added, we will check for these
default files. You can also change these after quick registration. They
will be applied to all versions that have not been edited, as well as
any new versions that may appear.
A tool is not visible on the public ‘Tools’ listing unless it is published. To publish a tool, press the ‘Publish’ button in the top-right corner.
For the tutorial, generally, you should hit the “Refresh All” button to make sure Dockstore has examined your latest repositories on Quay. This is how Dockstore picks up new repositories like we did here. (After the tutorial, you can refresh tools individually or by organization to speed things up)
Now select the collaboratory/dockstore-tool-bamstats repository and
click “Publish”. The tool is now listed on Dockstore!
You can also click on the “Versions” tab and should notice 1.25-6 is
present and valid. If any versions are invalid it is likely due to a
path issue to the Dockstore.cwl or Dockerfile. In BAMStats I used the default value
of Dockstore.cwl and Dockerfile in the root repo directory so
this was not an issue.
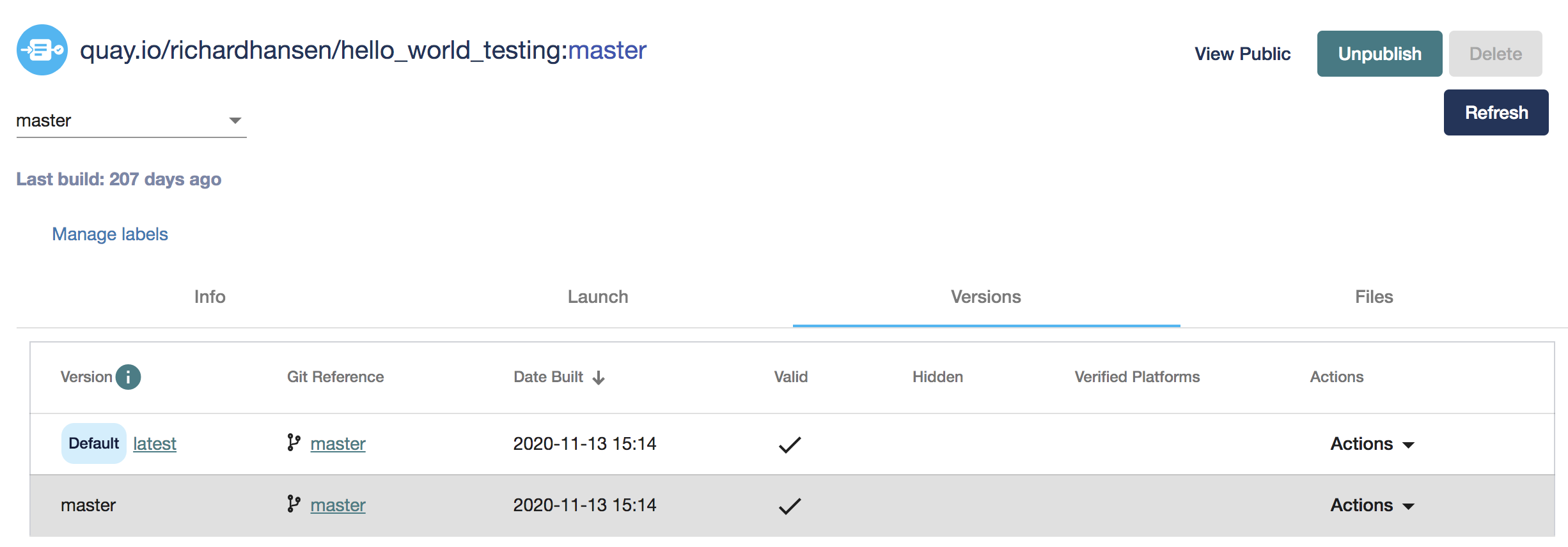
Publish
Next, pick a version of your tool that you wish to present to the world by opening the drop-down menu in the Version column, then selecting “set as default version.” This will determine which version of your CWL file will be used to find the author, email, and description in the case that it changes between versions. This also allows you to pre-select a version of your tool to present to users in the “Launch With” section, and the Dockerfile and Descriptor tabs.
Option B: Quick Registration of Alternate Tools
You may wish to re-register a pre-existing tool with a new name. This can occur when you’ve quick registered a tool, but wish to create a new tool with a different descriptor based on the same Docker image when your Docker image supports a number of different commands.
Consider the linked
repository.
If you’ve followed along some of our CWL tutorials, you will have this as a published tool.
But wait, there’s a Dockstore2.cwl in the same repo with a different
command.
To register this, follow the procedure below:
First, make note of the GitHub repository that stores the descriptors for the tool.
Second, hit the plus button on the top left and select ‘Create tool with
descriptor(s) on remote sites’. Ensure that the GitHub
repository and image registry match your previous tool. Note that we
changed the default CWL Descriptor Path to Dockstore2.cwl to
simulate an alternate descriptor for the same Docker image. Last but not
least, change the tool name to distinguish the tool from the intial
tool.
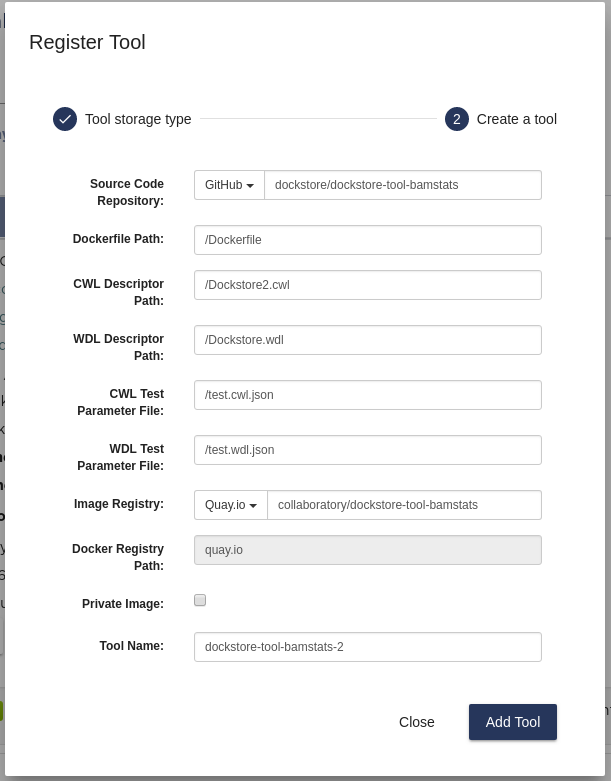
Add alternate tool
After clicking on “Add Tool” you should now see a new “Fully-Automated” tool that shared a GitHub and Quay.io repo with an existing tool. Note that the description and launch-with commands should reflect the new tool and the ID will have an additional part (up from three) identifying the new alternate tool.
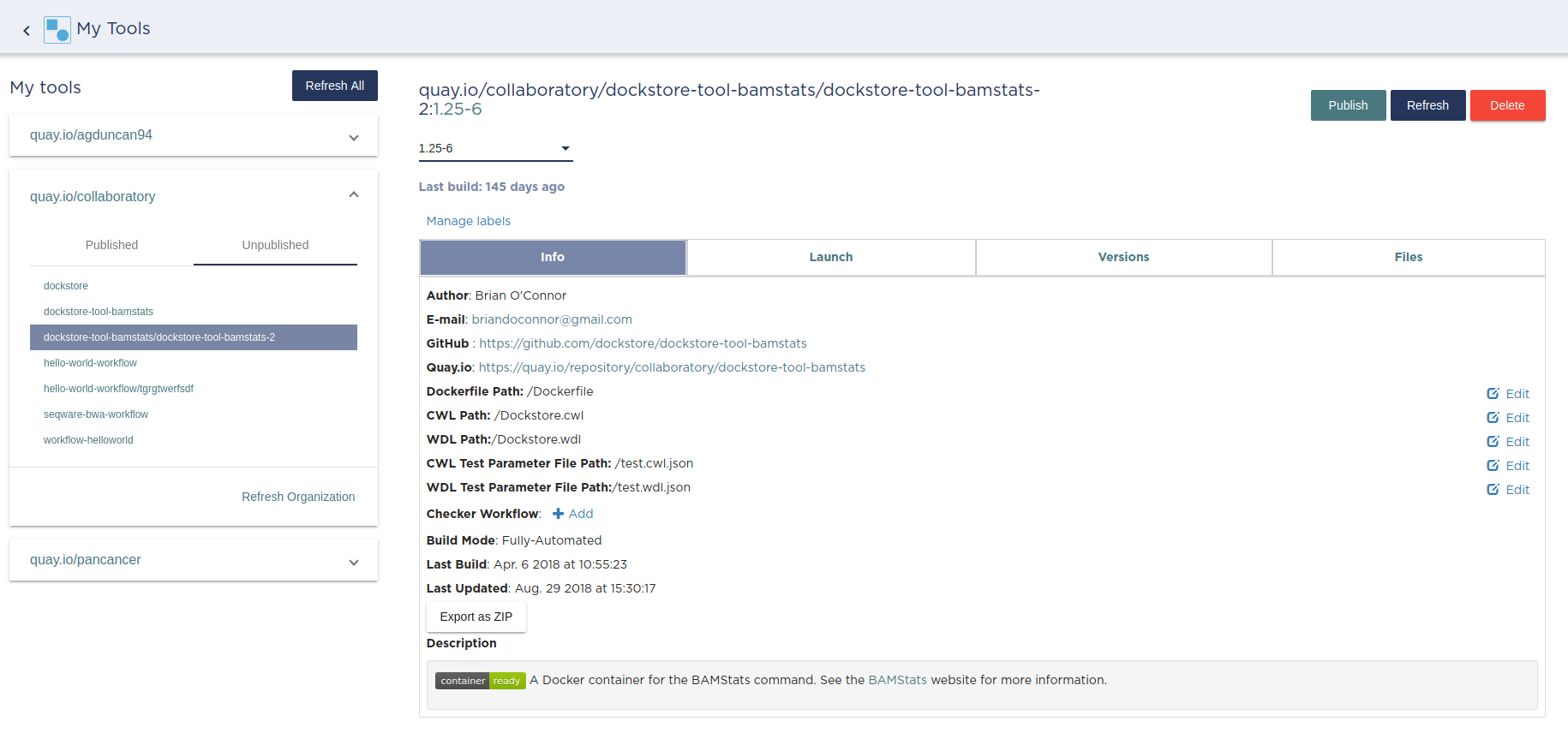
Newly created alternate tool
Option C: Manual Registration of Tools
Outside of this tutorial, in certain cases, it is not possible for Dockstore to register every existing tool, especially those with unusual project structures. Most notably, Docker Hub and GitLab images can not be automatically detected by Dockstore. The second possibility is that you have multiple CWL documents in a GitHub repository associated with multiple images. For those cases, it is necessary to manually register their details to Dockstore.
Tools can be registered manually from the ‘My Tools’ page by pressing the plus button at the top left of the page. A modal dialog will appear as below:
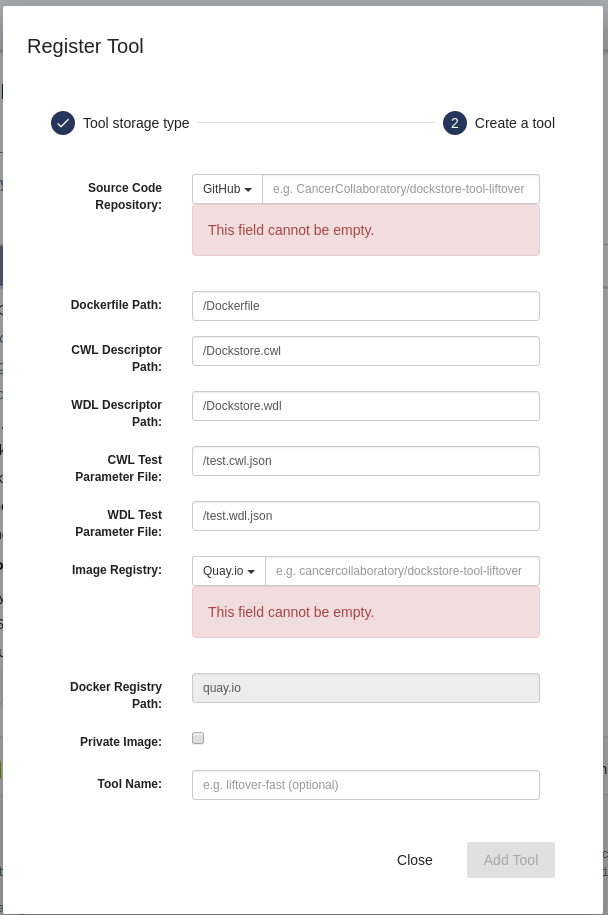
Register Tool Manual
Select ‘Use CWL, WDL or Nextflow from GitHub, BitBucket, etc’ and click next.
The Source Code Repository and Image Registry fields must be filled out,
and they are in the format namespace/name (the two paths may
differ). The Dockerfile Path, CWL Descriptor Paths, and CWL Test
Parameter Paths are relative to the root of the Source Code Repository
(and must begin with ‘/’). These will be the default locations to find
their corresponding files, unless specified otherwise in the tags. The
toolname is an optional ‘suffix’ appended to the Dockstore path. It
allows for two repositories to share the same Git and Image Registry
paths; the combination of Docker image registry path and toolname
uniquely distinguishes tools in Dockstore.
If you want to register a private Docker image and manage access, please click the “private” checkbox. You will also be asked for a tool maintainer email. This is the email of the person responsible for giving users access to your tool on external sites. If you do not provide a tool maintainer email, we will use the email found in the tool’s CWL descriptor instead, if provided.
Upon successful submission and registration of the tool, a resynchronization call will be made to fetch all available data from the given sources. If the image registry is Quay.io, existing version tags will be prepopulated for the Dockstore record.
Versions Grid
Press the ‘Add Tag’ button to begin creating tags for the different versions of the image. The tag creation modal will appear:
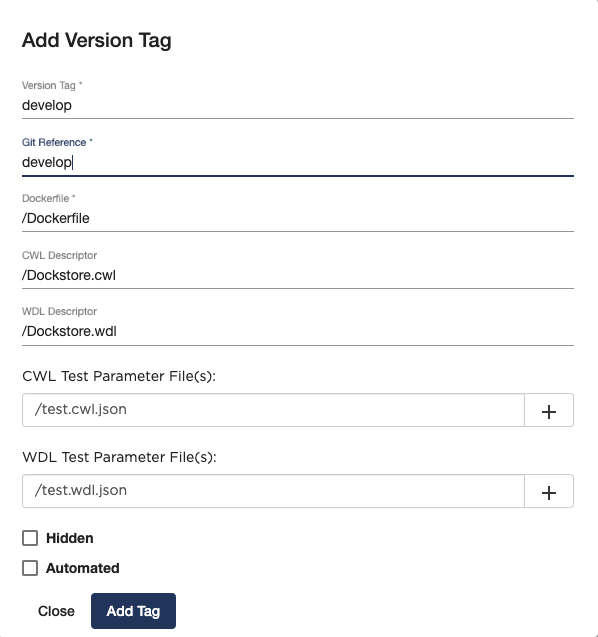
Edit Version Tag Dialogue
The fields in the form should correspond to the actual values on
GitHub/Bitbucket/GitLab and Quay.io/Docker Hub in order for the
information to be useful to other users. Selecting Hidden will
prevent the tag from appearing in the public listing of tags for the
image.
Option D: CLI Client
The Dockstore command line tool can be used as an alternative to the GUI and has two modes.
$ dockstore
HELP FOR DOCKSTORE
------------------
See https://www.dockstore.org for more information
Usage: dockstore [mode] [flags] [command] [command parameters]
Modes:
tool Puts dockstore into tool mode.
workflow Puts dockstore into workflow mode.
checker Puts dockstore into checker mode.
plugin Configure and debug plugins.
deps Print tool/workflow runner dependencies.
------------------
Flags:
--help Print help information
Default: false
--debug Print debugging information
Default: false
--version Print dockstore's version
Default: false
--server-metadata Print metdata describing the dockstore webservice
Default: false
--upgrade Upgrades to the latest stable release of Dockstore
Default: false
--upgrade-stable Force upgrade to the latest stable release of Dockstore
Default: false
--upgrade-unstable Force upgrade to the latest unstable release of Dockstore
Default: false
--config <file> Override config file
Default: ~/.dockstore/config
--script Will not check Github for newer versions of Dockstore
Default: false
--clean-cache Delete the Dockstore launcher cache to save space
------------------
First, we will work in tool mode (dockstore tool). We recommend you
first dockstore tool refresh to ensure the latest GitHub, Bitbucket,
GitLab and Quay.io information is indexed properly.
$ dockstore tool
HELP FOR DOCKSTORE
------------------
See https://www.dockstore.org for more information
Usage: dockstore tool [flags] [command] [command parameters]
Commands:
list : lists all the Tools published by the user
search : allows a user to search for all published Tools that match the criteria
publish : publish/unpublish a Tool in the dockstore
info : print detailed information about a particular published Tool
cwl : returns the Common Workflow Language Tool definition for this entry
which enables integration with Global Alliance compliant systems
wdl : returns the Workflow Descriptor Langauge definition for this Docker image.
refresh : updates your list of Tools stored on Dockstore or an individual Tool
label : updates labels for an individual Tool
test_parameter : updates test parameter files for a version of a Tool
convert : utilities that allow you to convert file types
launch : launch Tools (locally)
download : download Tools to the local directory
version_tag : updates version tags for an individual tool
update_tool : updates certain fields of a tool
manual_publish : registers a Docker Hub (or manual Quay) tool in the dockstore and then attempt to publish
------------------
Flags:
--help Print help information
Default: false
--debug Print debugging information
Default: false
--config <file> Override config file
Default: ~/.dockstore/config
--script For usage with scripts. Will not check for updates to Dockstore CLI.
Default: false
------------------
You can then use dockstore tool publish to see the list of available
Docker images you can register with Dockstore. This is for you to
publish tools that are auto-detected from Quay.io. The key is that
Docker images you wish to (quick) publish have the following qualities:
Public
At least one valid tag. In order to be valid, a tag has to:
be automated from a GitHub, Bitbucket, or GitLab reference
have the reference be linked to the
Dockerfilehave the reference be linked a corresponding
Dockstore.cwl
$ dockstore tool publish
YOUR AVAILABLE CONTAINERS
------------------
NAME DESCRIPTION Git Repo On Dockstore? Descriptor Automated
quay.io/cancercollaboratory/dockstore-tool-samtools-index Prints alignments in the specified input alignm... git@github.com:CancerCollaboratory/dockstore-tool-samtools-index.git No
Yes Yes
quay.io/cancercollaboratory/dockstore-tool-samtools-rmdup Remove potential PCR duplicates: if multiple re... git@github.com:CancerCollaboratory/dockstore-tool-samtools-rmdup.git No
Yes Yes
quay.io/cancercollaboratory/dockstore-tool-samtools-sort Sort alignments by leftmost coordinates, or by ... git@github.com:CancerCollaboratory/dockstore-tool-samtools-sort.git No
Yes Yes
quay.io/cancercollaboratory/dockstore-tool-samtools-view Prints alignments in the specified input alignm... git@github.com:CancerCollaboratory/dockstore-tool-samtools-view.git No
Yes Yes
quay.io/cancercollaboratory/dockstore-tool-snpeff Annotates and predicts the effects of variants ... git@github.com:CancerCollaboratory/dockstore-tool-snpeff.git No
Yes Yes
$ dockstore tool publish --entry quay.io/cancercollaboratory/dockstore-tool-snpeff
Successfully published quay.io/cancercollaboratory/dockstore-tool-snpeff
You can see in the above, the tool (identified with
quay.io/cancercollaboratory/dockstore-tool-snpeff in Dockstore and
Quay.io) was successfully registered and can be seen by anyone on the
Dockstore site.
The dockstore tool manual_publish command can be used to manually
register a tool on Docker Hub. Its usage is outlined in the
publish_manual help menu. This will allow you to register entries that
do not follow the qualities above (non-automated builds and Docker Hub
images).
$ dockstore tool manual_publish --help
HELP FOR DOCKSTORE
------------------
See https://www.dockstore.org for more information
Usage: dockstore tool manual_publish --help
dockstore tool manual_publish [parameters]
Description:
Manually register an tool in the dockstore. Currently this is used to register entries for images on Docker Hub.
Required parameters:
--name <name> Name for the docker container
--namespace <namespace> Organization for the docker container
--git-url <url> Reference to the git repo holding descriptor(s) and Dockerfile ex: "git@github.com:user/test1.git"
--git-reference <reference> Reference to git branch or tag where the CWL and Dockerfile is checked-in
Optional parameters:
--dockerfile-path <file> Path for the dockerfile, defaults to /Dockerfile
--cwl-path <file> Path for the CWL document, defaults to /Dockstore.cwl
--wdl-path <file> Path for the WDL document, defaults to /Dockstore.wdl
--test-cwl-path <test-cwl-path> Path to default test cwl location, defaults to /test.cwl.json
--test-wdl-path <test-wdl-path> Path to default test wdl location, defaults to /test.wdl.json
--toolname <toolname> Name of the tool, can be omitted, defaults to null
--registry <registry> Docker registry, can be omitted, defaults to DOCKER_HUB. Run command with no parameters to see available registries.
--version-name <version> Version tag name for Dockerhub containers only, defaults to latest.
--private <true/false> Is the tool private or not, defaults to false.
--tool-maintainer-email <tool maintainer email> The contact email for the tool maintainer. Required for private repositories.
--custom-docker-path <custom docker path> Custom Docker registry path (ex. registry.hub.docker.com). Only available for certain registries.
------------------
Additional Information on Build Modes
If you are using legacy registration, chances are you have set up an autobuilding Docker image. Here is more information on different build modes that are supported.
Fully-Automated (Quay.io Only)
How to create it:
Create by using the “Refresh All” button. This will scan through your Quay.io repositories and automatically register the tool on Dockstore.
Requirements:
Using a Quay.io registry with Quay.io linked to Dockstore.
Benefits:
This build mode automatically adds versions to your tool with Quay tags and their Git references by determining which tags on git were responsible for triggering builds on Quay.
Limitations:
Unable to easily deregister the tool
Unable to manually add versions
Cannot uniquely name the tool
Currently only works with Quay.io image registry
When to use:
Recommended when you are using a Quay.io registry, want a quick and easy way to register the tool, and want to avoid manually adding new versions to the tool. Generally recommended for most tools.
Note
If the Quay.io repository has at least one build that was not triggered by a git repository, then the tool will have the build mode Partially-Automated. The tool will still have the same benefits as a Fully-Automated tool.
Manual
How to create it:
Click Plus button on the top left of the screen
Requirements:
Registry that has at least one tag
Token to the corresponding registry (if using Quay.io)
Limitations:
Have to manually add the tool and also manually add each version (refresh will not work)
When to use:
Recommended when you’re not using Quay.io, someone else has the same tool name already and you want your own tool instead, or if you are not using build triggers.
Converting Between Build Modes (Quay.io Only)
Manual -> Fully-Automated:
Add a git build trigger to the Quay.io repository
Refresh the manual tool
Fully-Automated -> Manual:
Delete tool
Create a new manual tool (will have to recreate the Quay.io repository)
Note
When manually adding a Quay.io tool, if there exists a Fully-Automated tool on Dockstore with the same Docker image and Git repository as the manual tool, then the manual tool will be converted to Fully-Automated.