FAQ
For questions relating to the Dockstore CLI, please see Dockstore CLI FAQ.
Table of Contents
General Dockstore Questions
How do I use workflows that I find on Dockstore?
If you want to run the workflow locally, you can use the Dockstore CLI to download and run the workflow. Alternatively, you can run the workflow using a cloud platform by clicking the “Launch With” button on the right side of the workflow entry.
What is a verified tool or workflow?
A verified tool/workflow means that at least one version has been verified to be successfully ran on a platform.
See Verification for full details on this feature.
What is a default version of a tool or workflow?
Every tool/workflow is recommended to have a default version set by its author. It indicates to the end users which version of the tool/workflow they should use. For tools, the default version is uniquely identified by the tag from the Docker image repository. For workflows, the default version is identified by the Git Reference (which could be a Git tag or a Git branch). The default version can be set in the ‘Versions’ tab of a tool/workflow via radio buttons.
Setting the default version affects a number of elements including (but not limited to):
It determines what is displayed in the ‘Description’ section of the ‘Info’ Tab
It is the first version other end users see when no version is specified. For example https://dockstore.org/containers/quay.io/pancancer/pcawg-bwa-mem-workflow is redirected to https://dockstore.org/containers/quay.io/pancancer/pcawg-bwa-mem-workflow:develop?tab=info
It is the version of the tool/workflow that is launched by default when users launch a tool/workflow from the Dockstore CLI. For example, if version 1.0 is set as the default version of the quay.io/cancercollaboratory/dockstore-tool-bedgraph-bigwig tool,
$ dockstore tool launch --entry quay.io/cancercollaboratory/dockstore-tool-bedgraph-bigwig:1.0 --json Dockstore.jsonwould be equivalent to
$ dockstore tool launch --entry quay.io/cancercollaboratory/dockstore-tool-bedgraph-bigwig --json Dockstore.jsonThe docker pull command in the tools search reflects the default version
What is an Open Data tool or workflow version?
On Dockstore, an Open Data tool or workflow version includes everything needed to run the version, without any additional data access. This usually means there is a test parameter file whose file input parameter values only refer to open data – data that is not restricted access nor costs any money to download.
Note that tool and workflow versions that do not require any file input parameters are also considered Open Data.
You can find Open Data workflows and tools by selecting the Open Data facet on the search page. When viewing an individual tool or workflow, you can tell which versions are Open Data on the Versions tab via the Open column.
Note
Dockstore does not consider requester pays data such as Google Cloud Requester Pays and Amazon S3 Requester Pays to be open data. Even though their data may be open, our Open Data facet only shows those that are open and free.
How should I register my work in Dockstore?
Registering a CWL CommandLineTool?
Hosted on GitHub?
Register your tool to automatically sync using GitHub Apps
Hosted on BitBucket or GitLab?
Register using legacy tool registration methods or consider uploading your work to GitHub
Registering a CWL Workflow, WDL, Nextflow, or Galaxy descriptor files?
Hosted on GitHub?
Register your workflow to automatically sync using GitHub Apps
Hosted on BitBucket or GitLab?
Register using legacy workflow registration methods or consider uploading your work to GitHub
How do I send private messages to administrators or report security vulnerabilities?
Use the “Report a vulnerability” button on the upper right of this page on GitHub to report security vulnerabilities.
A helpdesk ticket may be an option for privacy complaints or other urgent non-security matters. Both options will be addressed by Dockstore administrators. The following steps can be taken to create a helpdesk ticket (also shown here).
Navigate to Discourse and login.
Select your profile icon, located in the top right corner of the screen.
Select the
mailicon, located in the dropdown.Send a message to the
dockstore_adminsgroup.
Note
If you are unable to see a New Message button on the mail page, you may be considered a new user and have insufficient privileges. Entering 5 topics and viewing 30 posts over a minimum of 10 minutes will raise your privileges. You will be notified of any privilege changes to your account via the mailbox.
How do I cite Dockstore?
For citing Dockstore as a paper, take a look at our Nucleic Acids Research paper or our older F1000 paper.
For citing the actual code, we recommend looking at our Zenodo entry.
You will find a variety of citation styles and ways to export it at
.
Integration with GitHub
What is the difference between logging in with GitHub versus logging in with Google?
The intent here is that you should be able to login with either login method and still conveniently get into the same Dockstore account. With login via Google, if you are a Terra user you will also have access to sharing functionality.
Note that for simplicity, each of your GitHub or Google accounts can only be associated with one account at a time. You will need to link with a different account for each login method or delete your account if you want to assign them to a new Dockstore account.
What happens if I rename my GitHub repository?
When you have registered a tool or workflow from GitHub in Dockstore the link to the repository for your tool or workflow is displayed on the Info tab next to ‘Source Code’. If you then rename the GitHub repository, the Source Code link will display the original name, but will resolve to the correct GitHub location when you click on it.
Another side effect is that you will be able to register the workflow again in Dockstore under the new GitHub name, so you effectively will have registered the same workflow twice.
Please note the GitHub warning: If you create a new repository under your account in the future, do not reuse the original name of the renamed repository. If you do, redirects to the renamed repository will break.
Permissions
How do I add other users as maintainers of a workflow?
For workflows registered with GitHub, Dockstore allows users from the same GitHub organization to manage workflows together. If a new GitHub workflow from the same GitHub organization is added to Dockstore by another user, click the “Discover Existing Dockstore Workflows” button in the “My Workflows” menu so the workflow will appear in My Workflows.
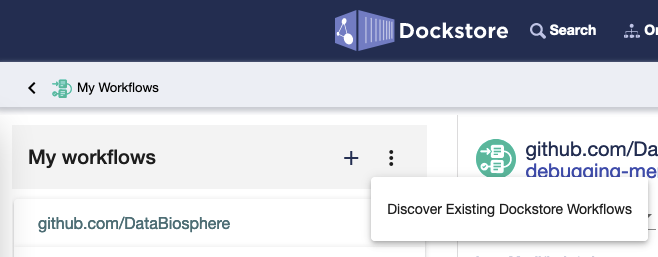
If the workflow was added by manually registering it, click Refresh Organization.
For participants of the limited sharing preview, you can enter the email addresses of the users you wish to share with to give them permissions to your workflow. This is only available for hosted workflows and users with Google accounts linked to Terra.
Why are my workflows from an organization I belong to not visible?
Organizations have the ability to restrict access to the API for third party applications. GitHub provides a tutorial on how to add these restrictions to your organizations. For recently-created GitHub organizations, third party application access is denied by default.
In order for Dockstore to gain access to organizations of this type, you will need to grant access to the Dockstore application. Dockstore will only be reading information on workflows in your organization and who has access to them in order to mirror these restrictions on Dockstore itself. GitHub provides a tutorial for approving third party apps access to your organization.
As you navigate GitHub’s administrative interface, you may see a message indicating that you have denied Dockstore access to your organization:
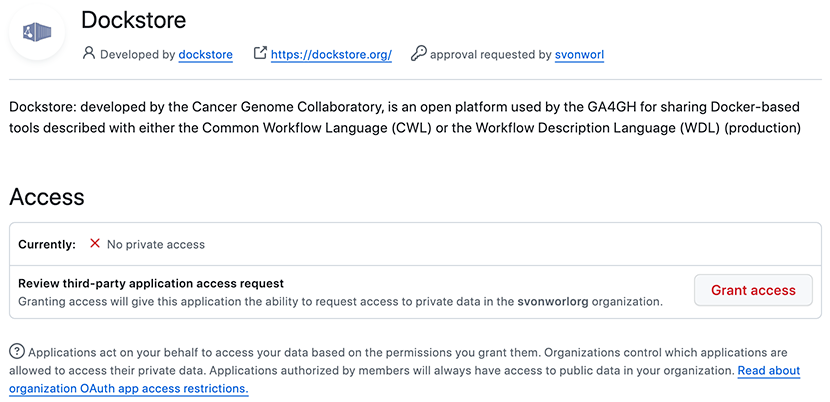
To grant access to the Dockstore application, click the Grant access button.
If you don’t grant access, some Dockstore functionality, such as manual workflow registration and the “Discover Existing Dockstore Workflows” feature, may not work properly for Dockstore users from your GitHub organization.
Why do I get an error when I try to request a DOI?
The following error occurs when another user from your GitHub organization has already requested a DOI for a workflow version belonging to the same workflow.

You are unable to request a DOI because you do not have the permission to create a deposition version for the Zenodo deposit that the other user created and owns. Until Zenodo supports the sharing of deposits, only one user of an organization is able to request a DOI. This user is the user who is first to request a DOI for the workflow.
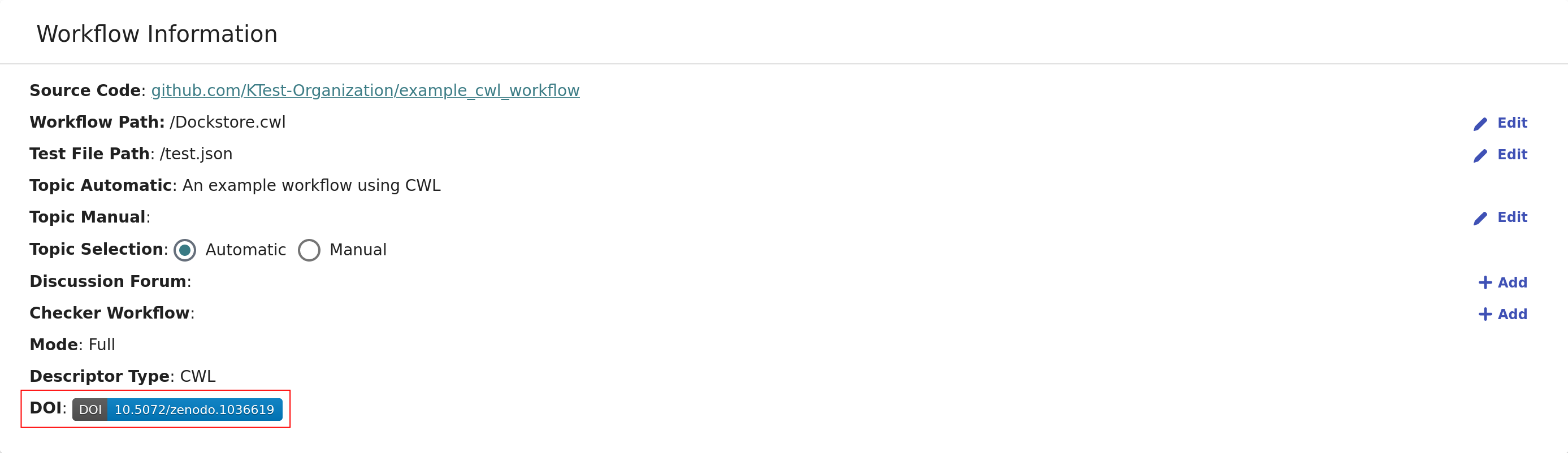
You must ask the user from your organization who already requested a DOI for a workflow version to request a DOI for the workflow version you want. You may view the DOI on Zenodo to see who created the DOI by clicking on the workflow DOI or workflow version DOI.
The workflow DOI can be found on the Info tab.
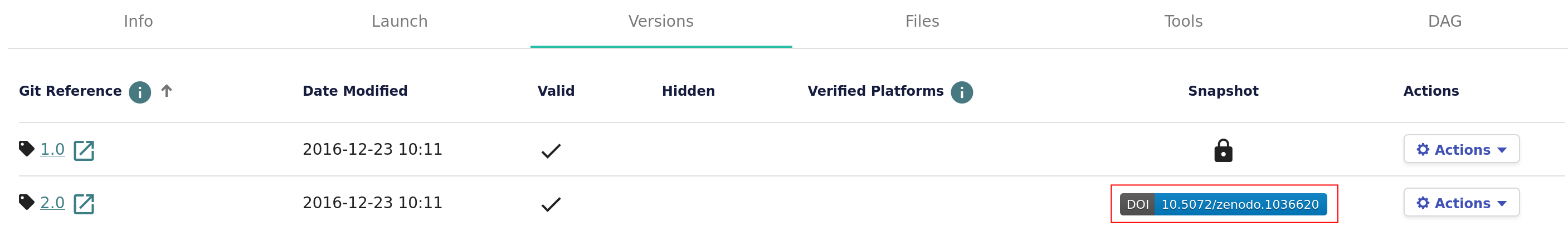
The workflow version DOI can be found on the Versions tab.
Other
There are too many versions of my tool, how do I delete some?
Versions of your tool for most tools are harvested from the list of Tags for an image on Quay.io, as an example. If you have the right permissions, you can delete some and then refresh a tool on Dockstore to clean-up.
How do I get more space inside my CWL tool running in a container?
There are a couple different answers here. Different directories inside a container run by CWL are mounted from different locations and will impose different storage requirements.
Outside the container, the Dockstore CLI will create a directory called
datastore which contains input files provisioned for the running
container. For CWL tools, this directory will include the working
directory (datastore/<uuid>/working), the temporary directory
(datastore/<uuid>/tmp/<random>), and input files
(datastore/<uuid>/inputs).
For the exact breakdown, keep an eye on the invocation of cwltool when
launching a tool. For example, the following means that the containers
working directory is stored at
/media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/datastore/launcher-22838dbe-044e-4ee5-8532-4cf405222439/working/ZQn2hv
on the underlying host and the temporary directory at
/media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/datastore/launcher-22838dbe-044e-4ee5-8532-4cf405222439/tmp/H1xA_N:
$ dockstore tool launch --local-entry Dockstore.cwl --json sample_configs.local.actual.json
Creating directories for run of Dockstore launcher at: ./datastore//launcher-22838dbe-044e-4ee5-8532-4cf405222439
Provisioning your input files to your local machine
Downloading: #bam_input from rna.SRR948778.bam into directory: /media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/./datastore/launcher-22838dbe-044e-4ee5-8532-4cf405222439/inputs/8beb90df-f193-493c-b834-ed28973015e3
Calling out to cwltool to run your tool
Executing: cwltool --enable-dev --non-strict --outdir /media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/./datastore/launcher-22838dbe-044e-4ee5-8532-4cf405222439/outputs/ --tmpdir-prefix /media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/./datastore/launcher-22838dbe-044e-4ee5-8532-4cf405222439/tmp/ --tmp-outdir-prefix /media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/./datastore/launcher-22838dbe-044e-4ee5-8532-4cf405222439/working/ /media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/Dockstore.cwl /media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/./datastore/launcher-22838dbe-044e-4ee5-8532-4cf405222439/workflow_params.json
/usr/local/bin/cwltool 1.0.20170217172322
Resolved '/media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/Dockstore.cwl' to 'file:///media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/Dockstore.cwl'
[job Dockstore.cwl] /media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/datastore/launcher-22838dbe-044e-4ee5-8532-4cf405222439/working/ZQn2hv$ docker \
run \
-i \
--volume=/media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/./datastore/launcher-22838dbe-044e-4ee5-8532-4cf405222439/inputs/8beb90df-f193-493c-b834-ed28973015e3/rna.SRR948778.bam:/var/lib/cwl/stgc2b37b55-005a-43e5-a824-6caf6656d9c2/rna.SRR948778.bam:ro \
--volume=/media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/datastore/launcher-22838dbe-044e-4ee5-8532-4cf405222439/working/ZQn2hv:/var/spool/cwl:rw \
--volume=/media/dyuen/Data/large_volume/datastore/launcher-22838dbe-044e-4ee5-8532-4cf405222439/tmp/H1xA_N:/tmp:rw \
--workdir=/var/spool/cwl \
--read-only=true \
--user=1001 \
--rm \
--env=TMPDIR=/tmp \
--env=HOME=/var/spool/cwl \
quay.io/collaboratory/dockstore-tool-bamstats:1.25-6_1.0 \
bash \
/usr/local/bin/bamstats \
4 \
/var/lib/cwl/stgc2b37b55-005a-43e5-a824-6caf6656d9c2/rna.SRR948778.bam
...
Also be aware that some tools will use space from your root filesystem. For example, Docker’s storage driver and data volumes will by default install to and use space on your root filesystem.
Do you have tips on creating Dockerfiles?
make sure you manage Docker as a non-root user on your system so you do not need sudo for the
dockercommanddo not call Docker-inside-Docker (it’s possible but causes Docker client/server issues, it is also not compatible with CWL)
do not depend on changes to
hostnameor/etc/hosts, Docker will interfere with thisuse a well-known and secure parent image such as official debian or Python images
try to keep your Docker images small - however, do not use alpine images, or other images that lack bash, as your parent image unless you will be installing bash in the Dockerfile
How should I handle large reference files when designing workflows and Dockerfiles?
Generally speaking, you can choose to either “package” reference files in your Docker image, or you can treat them as “inputs” so they can be staged outside and mounted into the running container. We generally recommend having them serve as inputs.
Do you have tips on creating workflows?
When writing workflows, there are a few common workarounds that can be used to deal with the restrictions that workflow languages such as CWL and WDL place on the use of Docker. These include:
cwltool (which we use to run tools) is restrictive and locks down much of
/as read only, use the current working directory or $TMPDIR for file writesYou can also use Docker volumes in your Dockerfile to specify additional writeable directories
Do not rely on the hostname inside a container; Docker dynamically generates this when starting containers
Do not rely on an entrypoint inside a container; workflow executors tend to override custom entrypoints with /bin/bash
Additionally:
in order for the workflow executor to “find” your outputs and pull them back outside the container, you may want to “collect” output from your tools/workflows inside Docker and drop them into the current working directory
related to this, it’s often times easiest to write a simple wrapper script that maps the command line arguments specified by CWL to however your tool expects to be parameterized. This script can handle moving output to the current working directory and renaming if need be
Why would I want to add a specific version of a workflow to a collection?
When creating a collection in an organization, you can pin either a specific version of a workflow or add the workflow in general. This is a flexible system and can mean different things to different organizations. You can elaborate on what this means to you as an organization maintainer in the markdown description associated with a collection.
As an example, if your organization is responsible for a workflow and its maintenance going forward, you may want to add the workflow to a collection without specifying a specific version. On the other hand, if you are creating an organization for a specific study and you are using a specific version of a workflow that has been screened for security issues and other measures of quality, you may want to pin the specific version of the workflow. You also have the option of adding a workflow to a collection multiple times by bringing up the add dialog if multiple versions of the workflow have been vetted.
Note that the version of a workflow can be especially important when working with launch-with partners. Some partners will take into account the version of the workflow that you are on wheras other partners will give the option of or require selecting the workflow version when performing a workflow launch. For example, Terra will automatically bring up the version you are currently browsing when performing a launch although you will have an option to override later in the process.
In summary: you can pin either a specific version of a workflow or a workflow in general depending on what relationship you wish to express. We recommend explaining further for others in the accompanying Markdown description.
Any last tips on using Dockstore?
the Dockstore CLI uses
./datastorein the working directory for temp files, so if you’re processing large files, make sure this partition hosting the current directory is large.you can use a single Docker image with multiple tools, each of them registered via a different CWL
you can also use a single Docker image with multiple workflows
you can use a Git repository with multiple workflow files
related to the two above, you can use non-standard file paths if you customize your registrations in the Version tab of Dockstore
What happens if I link to a different ORCID account?
ORCID is designed to discourage more than one account for an individual. However, if you somehow end up with two ORCID accounts, publish a record from Dockstore using the first ORCID account, then relink Dockstore to the second ORCID account, you will not be able to update the original ORCID record from within Dockstore.
If you run into this situation, please use the Help Desk link in the https://dockstore.org footer to contact the Dockstore team.