Getting Started with Galaxy
Dockstore supports Galaxy workflows and the Launch with Galaxy tutorial elaborates different ways to launch a Galaxy workflow. Please note that Galaxy workflows cannot be launched by the Dockstore CLI.
Tutorial Goals
Learn about Galaxy
Create and run a basic Galaxy workflow
Export the workflow to a file
Setup a GitHub account and repository
Push the workflow to GitHub
Make a GitHub release
About Galaxy
Galaxy is a web-based platform for data analysis. Galaxy is open source and can be installed locally. Alternatively, many institutions offer access to managed Galaxy instances, free and otherwise. Different Galaxy instances come with their own advantages and users can make a choice based on their own needs.
Using Existing Galaxy Servers
Institutions across the world maintain Galaxy instances that are shared with the greater community and are a great way to learn and use Galaxy. Some of these instances are subsidized by grants and offered for free (such as the Galaxy US, Galaxy EU, and Galaxy AU) and some are available for a fee (such as Galaxy AnVIL). A lot of great learning resources are available on the the Galaxy Training Network, with help on specific questions available via Galaxy Help.
Using Custom Galaxy in the Cloud with Terra, and AnVIL
Galaxy is also integrated into the Terra cloud workspace. This provides users the ability to readily create a custom Galaxy environment scaled to their needs or with additional tools installed. Additionally, the Terra workspace is able to access a rich data corpus hosted in the cloud, including many controlled access datasets, thus allowing users to conduct analyses with this data in a compliance-based environment.
Create a basic Galaxy workflow
Unlike other workflow languages such as WDL and CWL, Galaxy workflows are currently created and modified from the Galaxy workflow editor (GUI), instead of a text editor.
If you would like to create and run your own workflow in Galaxy, here is a tutorial for Creating, Editing, Importing Galaxy Workflows from the Galaxy Training Network.
In addition, the Galaxy Intergalactic Workflow Commission (IWC) team has an excellent tutorial for creating best practices workflows for IWC here. It discusses how to add the correct metadata, generate tests, and lint your workflow. It also shows how you can generate a .dockstore.yml using the Planemo command-line utilities.
Export the workflow to a file
Once you’ve created a workflow in Galaxy, you can export it. This is a required step to register the workflow with Dockstore.
Click on the Galaxy UI Workflow link at the top of the page.
Click on the workflow name to expose the drop down menu.
Click Download
The exported JSON file with a ‘.ga’ suffix describes the inputs, outputs, and Galaxy Tool Shed dependencies for your workflow.
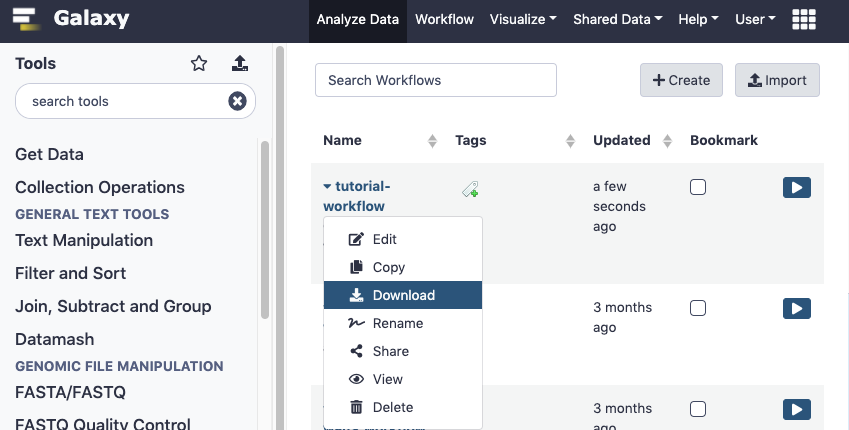
Download
Note
As of this writing, the Galaxy team has created an improved YAML-based file format, known as “Format 2”, that is more human-friendly and preferred over the original ‘.ga’ format. Currently, the Galaxy interface only exports files in the original ‘.ga’ format, but this may change. If the Galaxy interface allows it, you should export your Galaxy workflow as a “Format 2” file.
Setting up GitHub
You will need to add the Galaxy workflow file you downloaded to a source code repository that Dockstore knows about. GitHub is a good choice, and if you are not familiar with GitHub you can use this tutorial to set up an account and repository.
Upload the workflow to GitHub
Go to your repository and click on the Upload Files menu item under Add Files
Click on the ‘choose your files’ link
Select your exported Galaxy workflow file
Click on ‘Commit changes’
These steps are outlined here.
Add Test Parameter File
You can add a test parameter file to your source code repository, allowing other users to easily launch a test run of your workflow. Follow these instructions to create a test parameter file. Then, add the file you have created to your GitHub repository as you did with your exported Galaxy workflow file above.
Releasing on GitHub
Now that we’ve successfully created our workflow in Galaxy and uploaded it to GitHub, the workflow is ready to share with others. Making a release on GitHub will tag your GitHub repository with a version tag so you can always get back to this particular version of the workflow. Follow the steps outlined here to create a release.
Next Steps
Now that you have a git repository that includes a Galaxy workflow, the next step is to register it on Dockstore.
If you haven’t set up a Dockstore account follow the next tutorial to create an account on Dockstore and link to third party services, which includes GitHub. Then follow the instructions for workflow registration.
Note
The workflow registration instructions describe manually creating a .dockstore.yml, a file needed for integrating Dockstore and GitHub. For
Galaxy, it’s recommended you instead use Planemo to generate the .dockstore.yml.
Using Planemo to generate a .dockstore.yml
The command-line utility for Galaxy, Planemo, can generate a .dockstore.yml. Install Planemo, then generate the .dockstore.yml file by navigating to the directory containing your workflow and running:
$ planemo dockstore_init .